4주차 과제: 제어문
제어문
- 프로그램 코드의 실행 흐름에 따라 제어하는 구문
조건문
- 조건에 따라 코드의 실행 흐름을 제어하는 구문
if문
- 조건식이 참인 경우 실행
public class conditionalSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 90;
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A학점 입니다");
}
if (score < 90) {
System.out.println("A학점이 아닙니다");
}
}
}결과
A학점 입니다if-else 문
- 조건식의이 참인 경우 실행하고 거짓일때 else 문의 코드가 실행
public class conditionalSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 90;
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A학점 입니다");
} else {
System.out.println("A학점이 아닙니다");
}
}
}결과
A학점 입니다선택문
- 선택문은 일치하는 변수의 값에 따라서 결과를 도출 해낸다.
- 다중 if문 대신 사용하거나, if문을 여러개 사용하면 실행속도가 느려지는 우려가 있어서 사용한다
- switch 함수의 매개변수에 들어오는 값에 따라 코드를 실행한다.
public class conditionalSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 90;
switch (score) {
case 95:
System.out.println("A+");
break;
case 90:
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 85:
System.out.println("B+");
break;
}
}
}결과
A반복문
- 특정 조건에 만족할때 코드를 반복해서 실행시킨다
for 문
- 반복하는 횟수를 정해서 사용한다
public class loopSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0 ; i<9; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}결과
**0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8**while 문
- 조건이 참일때 동안 반복해서 실행한다. 반복 횟수가 정해져 있지않다
public class loopSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i < 10) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}do-while 문
- 처음 한번 do절은 무조건 실행을 하고 다음 while문에 조건에 따라서 실행하는 구문이다
public class loopSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (i < 10) ;
}
}결과
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9과제 0. JUnit 5
- JUnit은 자바 프로그래밍 언어용 유닛 테스트 프레임워크이다. JUnit은 테스트 주도 개발 면에서 중요하며, SUnit과 함께 시작된 XUnit이라는 이름의 유닛 테스트 프레임워크 계열의 하나이다.
- JUnit은 단위 테스트를 위한 테스트용 프레임워크이다
- Java 8 이상의 새로운 기능을 지원한다
Java 11 기준
Gradle 의존성 추가
build.grade 추가
dependencies {
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.6.0'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine'
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}Maven 의존성 추가
pom.xml 추가
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.6.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>과제 1. live-study 대시 보드를 만드는 코드를 작성하세요.
- 깃헙 이슈 1번부터 18번까지 댓글을 순회하며 댓글을 남긴 사용자를 체크 할 것.
- 참여율을 계산하세요. 총 18회에 중에 몇 %를 참여했는지 소숫점 두자리가지 보여줄 것.
- Github 자바 라이브러리를 사용하면 편리합니다.
- 깃헙 API를 익명으로 호출하는데 제한이 있기 때문에 본인의 깃헙 프로젝트에 이슈를 만들고 테스트를 하시면 더 자주 테스트할 수 있습니다.
String token = "";
GitHub gitHub = new GitHubBuilder().withOAuthToken(token).build();
GHRepository repo = gitHub.getRepository("whiteship/live-study");
// 전체 이슈 18개
List<GHIssue> issues = repo.getIssues(ALL);
// 전체 참가자
Map<String, Integer> participantI = new HashMap<>();
for (GHIssue issue : issues) {
List<GHIssueComment> comments = issue.getComments();
Set<String> names = new HashSet<>();
for (GHIssueComment comment : comments) {
String name = comment.getUser().getLogin();
names.add(name);
}
for (String user : names) {
if (participantI.containsKey(user)) {
Integer cnt = participantI.get(user)+1;
participantI.put(user,cnt);
} else {
participantI.put(user, 1);
}
}
}
participantI.forEach(
(s, integer) -> {
System.out.println(s+" = "+String.format("%.2f", (float) integer / 18)+"%");
}
);결과
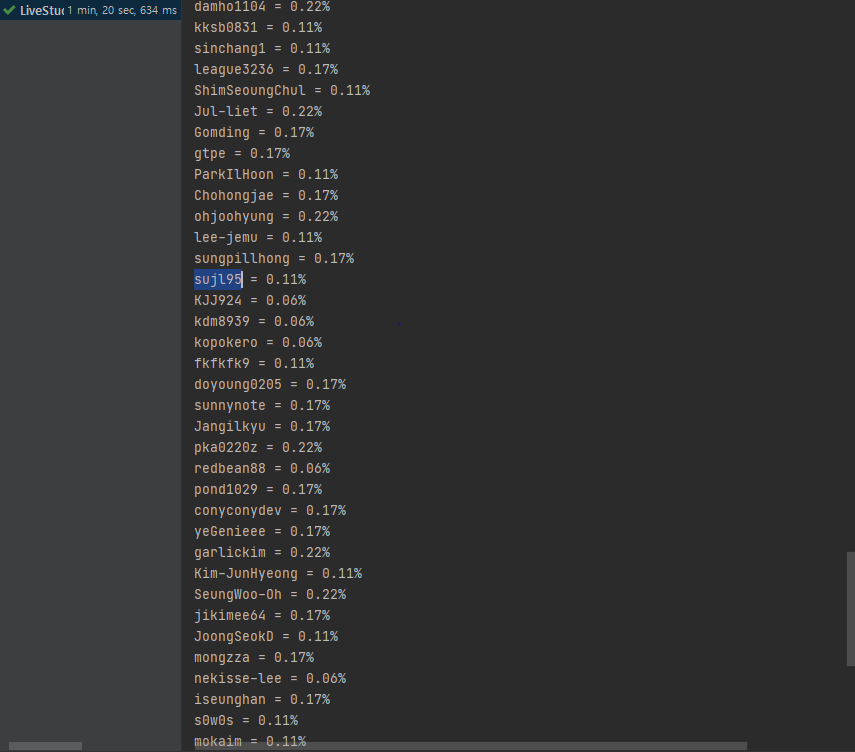
코드
https://github.com/sujl95/LiveStudy/blob/main/src/main/java/LiveStudy/_4Week/GithubSample.java
과제 2. LinkedList를 구현하세요.
- LinkedList에 대해 공부하세요.
- 정수를 저장하는 ListNode 클래스를 구현하세요.
- ListNode add(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToAdd, int position)를 구현하세요.
- ListNode remove(ListNode head, int positionToRemove)를 구현하세요.
- boolean contains(ListNode head, ListNode nodeTocheck)를 구현하세요.
LinkedList
노드 간에 연결(link)을 통해서 리스트로 구현된 객체이다. 다음 노드의 위치 정보만 가지고 있으며 인덱스를 가지고 있지 않기 때문에 탐색시 순차접근만 가능 (노트 탐색 시 시간이 많이 소요될 수 있음)(randomAccess 불가능)노드 추가/삭제는 위치정보의 수정만으로 가능하기 때문에 성능이 좋음
LinkedList는 ArrayList와는 달리 List 인터페이스를 구현한 AbstractList를 상속하지 않고 AbstractSequentialList를 상속한다.

LinkedList의 삽입/삭제 과정
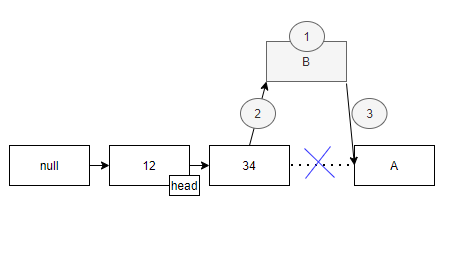
- 추가될 자료의 node 를 생성
- 추가될 자료의 해당 인덱스 이전의 node의 다음 node를 추가될 node로 지정
- 추가될 node의 다음 node를 인덱스 이전 node의 다음 node로 지정

- 삭제할 node[34] 의 이전 node[12]의 다음 node를 삭제할 node[33]의 다음 node[A]로 지정
구현
package LiveStudy._4Week;
public class ListNode {
/**
* ListNode add(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToAdd, int position)를 구현하세요.
* ListNode remove(ListNode head, int positionToRemove)를 구현하세요.
* boolean contains(ListNode head, ListNode nodeTocheck)를 구현하세요.
*/
private int data;
private boolean headCk;
private ListNode next;
private int size = 0;
public ListNode() {
headCk = true;
}
public ListNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
/**
*
* @param head
* @param nodeToAdd
* @param position
* @return
*/
public ListNode add(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToAdd, int position) {
if (position == 0) {
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = nodeToAdd;
nodeToAdd.next = temp;
return nodeToAdd;
}
if (head.next != null) {
return add(head.next, nodeToAdd, position-1);
}
head.next = nodeToAdd;
size++;
return nodeToAdd;
}
/**
* 현재 사이즈 보다 큰 값이 들어올 경우 마지막 노드의 값을 삭제한다
* @param head
* @param positionToRemove
* @return
*/
public ListNode remove(ListNode head, int positionToRemove) {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("size = 0");
return null;
}
ListNode temp = head;
int sizeCk = positionToRemove > size ? size : positionToRemove;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeCk-1; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
ListNode temp1 = temp.next;
temp.next = temp1.next;
temp1.next = null;
size--;
return head;
}
public boolean contains(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToCheck) {
ListNode temp = head.next;
if (temp == null) return false;
if(temp.data == nodeToCheck.data) return true;
else return contains(temp, nodeToCheck);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (next != null) {
if (headCk) {
return "--start\n"+next.toString();
}
return data+"\n"+next.toString();
}
return data+"\n--end";
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
}Run
ListNode head = new ListNode();
head.add(head , new ListNode(5), 1);
head.add(head , new ListNode(6), 2);
head.add(head , new ListNode(7), 3);
head.remove(head, 3);
head.remove(head, 5);
System.out.println(head.contains(head, new ListNode(5)));
System.out.println(head.contains(head, new ListNode(3)));
System.out.println(head.contains(head, new ListNode(7)));
System.out.println(head.getSize());
System.out.println(head.toString());결과
true
false
false
1
--start
5
--end과제 3. Stack을 구현하세요.
- int 배열을 사용해서 정수를 저장하는 Stack을 구현하세요.
- void push(int data)를 구현하세요.
- int pop()을 구현하세요.
구현
package LiveStudy._4Week;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ListNodeStack {
/**
* int 배열을 사용해서 정수를 저장하는 Stack을 구현하세요.
* void push(int data)를 구현하세요.
* int pop()을 구현하세요.
*/
int[] data;
int size;
int pos;
public ListNodeStack() {
this.size = 10;
this.data = new int[size];
this.pos = 0;
}
/**
* 생성할때 0번째 값 지정
* @param data
*/
public ListNodeStack(int data) {
this.size = 10;
this.data = new int[size];
this.pos = 1;
this.data[0] = data;
}
public void push(int data) {
if (this.size == this.pos +1) {
int[] newData = new int[size + 10];
for (int i = 0; i< size; ++i) newData[i] = this.data[i];
size += 10;
this.data = newData;
}
this.data[this.pos++] = data;
}
public int pop() {
if (this.pos == 0) {
System.out.println("size = 0");
return -1;
}
int resData = data[this.pos-1];
data[this.pos-1] = 0;
--this.pos;
return resData;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ListNodeStack{" +
"data=" + Arrays.toString(data) +
", size=" + size +
", pos=" + pos +
'}';
}
}실행
package LiveStudy._4Week;
public class ListNodeStackSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNodeStack stack = new ListNodeStack();
stack.push(0);
stack.push(0);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6);
stack.push(7);
stack.push(8);
stack.push(9);
stack.push(10);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.toString());
}
}결과
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
size = 0
-1
ListNodeStack{data=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], size=20, pos=0}과제 4. 앞서 만든 ListNode를 사용해서 Stack을 구현하세요.
- ListNode head를 가지고 있는 ListNodeStack 클래스를 구현하세요.
- void push(int data)를 구현하세요.
- int pop()을 구현하세요.
구현
package LiveStudy._4Week;
public class ListNodeStack2 {
ListNode head;
int size = 0;
public ListNodeStack2() {
head = new ListNode();
}
public void push(int data) {
head.add(head, new ListNode(data), size++);
}
public int pop() {
try {
head.remove(head, size--);
return head.getData();
} catch (Exception e) {
return -1;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return ""+head;
}
}실행
public class ListNodeStackSample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNodeStack2 stack = new ListNodeStack2();
stack.push(0);
stack.push(0);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6);
stack.push(7);
stack.push(8);
stack.push(9);
stack.push(10);
System.out.println(stack.toString());
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack.toString());
}
}결과
--start
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
--end
--start
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
--end과제 5. Queue를 구현하세요.
- 배열을 사용해서 한번
- ListNode를 사용해서 한번.
'스터디 > LiveStudy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7주차 과제: 패키지 (0) | 2020.12.30 |
|---|---|
| 6주차 과제: 상속 (0) | 2020.12.21 |
| 5주차 과제: 클래스 (0) | 2020.12.19 |
| 2주차 자바 데이터 타입, 변수 그리고 배열 (0) | 2020.11.20 |
| 1주차 과제: JVM은 무엇이며 자바 코드는 어떻게 실행하는 것인가. (0) | 2020.11.20 |